Before entering the room or during the call, you can check the user's network quality to determine the current network quality. If the user's network quality is too poor, it is recommended that the user change the network environment to ensure normal call quality.
This article mainly introduces how to implement network quality detection before the call or during the call based on the NETWORK_QUALITY event.
Detect network quality during the call
See: NETWORK_QUALITY
const trtc = TRTC.create();
trtc.on(TRTC.EVENT.NETWORK_QUALITY, event => {
console.log(`network-quality, uplinkNetworkQuality:${event.uplinkNetworkQuality}, downlinkNetworkQuality: ${event.downlinkNetworkQuality}`)
console.log(`uplink rtt:${event.uplinkRTT} loss:${event.uplinkLoss}`)
console.log(`downlink rtt:${event.downlinkRTT} loss:${event.downlinkLoss}`)
})
Detect network quality before the call
Implementation process
- Call TRTC.create to create two TRTC objects, referred to as uplinkTRTC and downlinkTRTC.
- Both TRTC objects enter the same room.
- Use uplinkTRTC to startLocalVideo, and listen to the NETWORK_QUALITY event to detect the uplink network quality.
- Use downlinkTRTC to startRemoteVideo, and listen to the NETWORK_QUALITY event to detect the downlink network quality.
- The entire process lasts for about 15 seconds, and finally takes the average network quality to roughly determine the uplink and downlink network conditions.
Notice:
- The detection process will generate a small amount of basic service fees. If the push stream resolution is not specified, it defaults to pushing the stream with a resolution of 640*480.
API call sequence
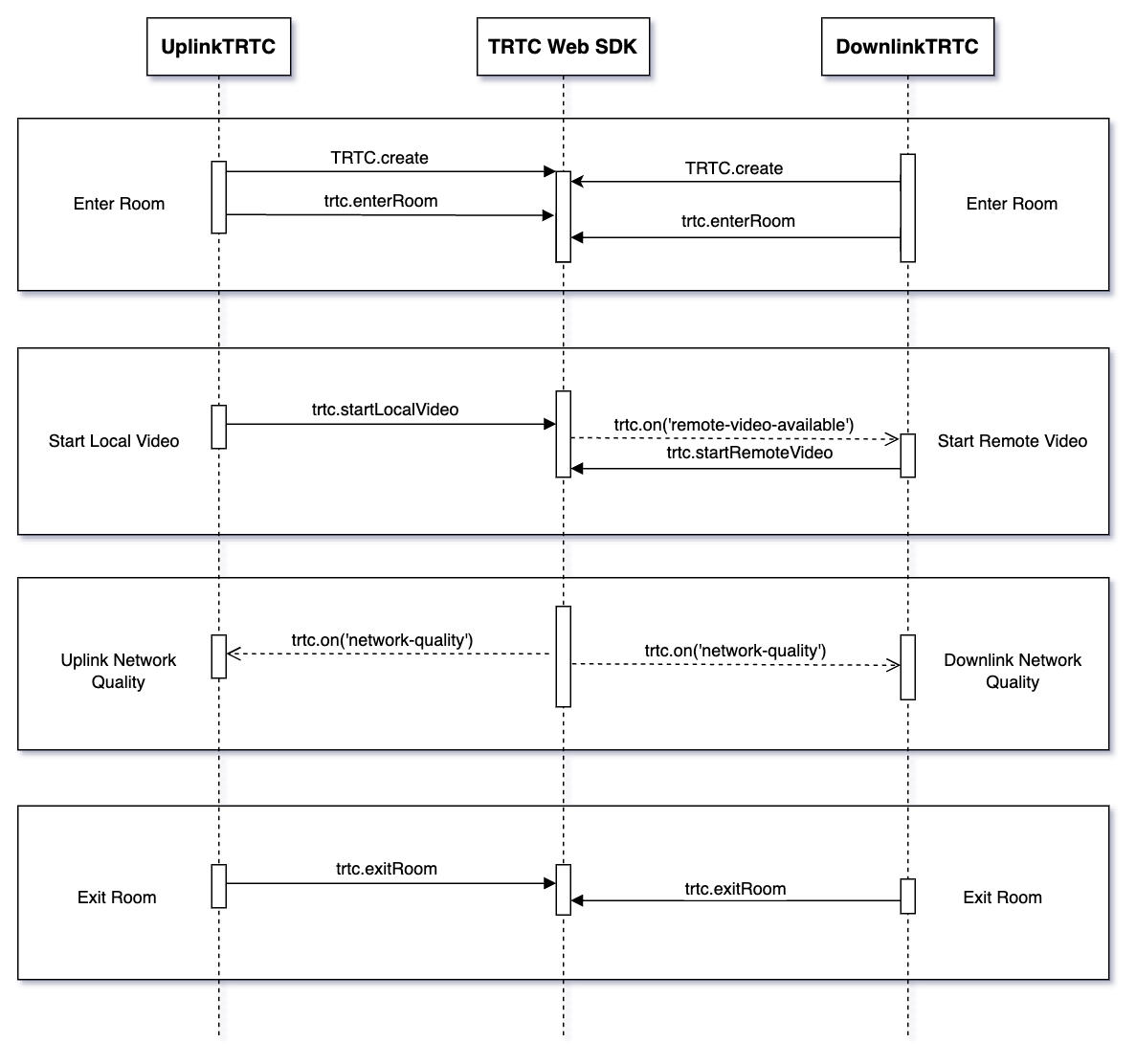
Code example
let uplinkTRTC = null; // Used to detect uplink network quality
let downlinkTRTC = null; // Used to detect downlink network quality
let localStream = null; // Stream used for testing
let testResult = {
// Record uplink network quality data
uplinkNetworkQualities: [],
// Record downlink network quality data
downlinkNetworkQualities: [],
average: {
uplinkNetworkQuality: 0,
downlinkNetworkQuality: 0
}
}
// 1. Test uplink network quality
async function testUplinkNetworkQuality() {
uplinkTRTC = TRTC.create();
uplinkTRTC.enterRoom({
roomId: 8080,
sdkAppId: 0, // Fill in sdkAppId
userId: 'user_uplink_test',
userSig: '', // userSig of uplink_test
scene: 'rtc'
})
uplinkTRTC.on(TRTC.EVENT.NETWORK_QUALITY, event => {
const { uplinkNetworkQuality } = event;
testResult.uplinkNetworkQualities.push(uplinkNetworkQuality);
});
uplinkTRTC.startLocalVideo();
}
// 2. Detect downlink network quality
async function testDownlinkNetworkQuality() {
downlinkTRTC = TRTC.create();
downlinkTRTC.enterRoom({
roomId: 8080,
sdkAppId: 0, // Fill in sdkAppId
userId: 'user_downlink_test',
userSig: '', // userSig
scene: 'rtc',
autoReceiveVideo: true
});
downlinkTRTC.on(TRTC.EVENT.NETWORK_QUALITY, event => {
const { downlinkNetworkQuality } = event;
testResult.downlinkNetworkQualities.push(downlinkNetworkQuality);
})
}
// 3. Start detection
testUplinkNetworkQuality();
testDownlinkNetworkQuality();
// 4. Stop detection after 15s and calculate the average network quality
setTimeout(() => {
// Calculate the average uplink network quality
const validUplinkNetworkQualitiesList = testResult.uplinkNetworkQualities.filter(value => value >= 1 && value <= 5);
if (validUplinkNetworkQualitiesList.length > 0) {
testResult.average.uplinkNetworkQuality = Math.ceil(
validUplinkNetworkQualitiesList.reduce((value, current) => value + current, 0) / validUplinkNetworkQualitiesList.length
);
}
const validDownlinkNetworkQualitiesList = testResult.uplinkNetworkQualities.filter(value => value >= 1 && value <= 5);
if (validDownlinkNetworkQualitiesList.length > 0) {
// Calculate the average downlink network quality
testResult.average.downlinkNetworkQuality = Math.ceil(
validDownlinkNetworkQualitiesList.reduce((value, current) => value + current, 0) / validDownlinkNetworkQualitiesList.length
);
}
// Detection is over, clean up related states.
uplinkTRTC.exitRoom();
downlinkTRTC.exitRoom();
}, 15 * 1000);
Result Analysis
After the above steps, you can get the average uplink network quality and the average downlink network quality. The enumeration values of network quality are as follows:
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 0 | The network condition is unknown, indicating that the current TRTC instance has not established an uplink/downlink connection |
| 1 | The network condition is excellent |
| 2 | The network condition is good |
| 3 | The network condition is average |
| 4 | The network condition is poor |
| 5 | The network condition is extremely poor |
| 6 | The network connection has been disconnected. Note: If the downlink network quality is this value, it means that all downlink connections have been disconnected. |
Suggestion: When the network quality is greater than 3, it is recommended to guide the user to check the network and try to change the network environment, otherwise it is difficult to ensure normal audio and video communication. You can also reduce bandwidth consumption through the following strategies:
- If the uplink network quality is greater than 3, you can reduce the bitrate through the TRTC.updateLocalVideo() interface or close the video through the TRTC.stopLocalVideo() method to reduce uplink bandwidth consumption.
- If the downlink network quality is greater than 3, you can reduce the downlink bandwidth consumption by subscribing to a small stream (refer to: Enable Small Stream Transmission) or only subscribing to audio.